Python
Lecture 17 - February 21st, 2017
Python Programming
- You can install python on your own computer.
- To execute a program:
- python
- python
print: is a function and strings are surrounded by quotes ""
Function: is a block of code that is grouped together
- The name makes it easy to execute
- Otherwise we'd have to copy and paste the same code multiple times
- Functions help organize
- Name Flowchart
- Functions can input values and return values
- We can write our own
- "def" to signal we are about to define a function
- Input parameters are in parenthesis, followed by colon
- All code in the function is indented.
Variables: name for a value, can change, variable is like a box
ex.
x = 5
Comments: Allows us to document our code
- Leave notes to you and others (not the computer)
ex.
# Here's a comment
x = 5
# Hey! Comment
Collatz:
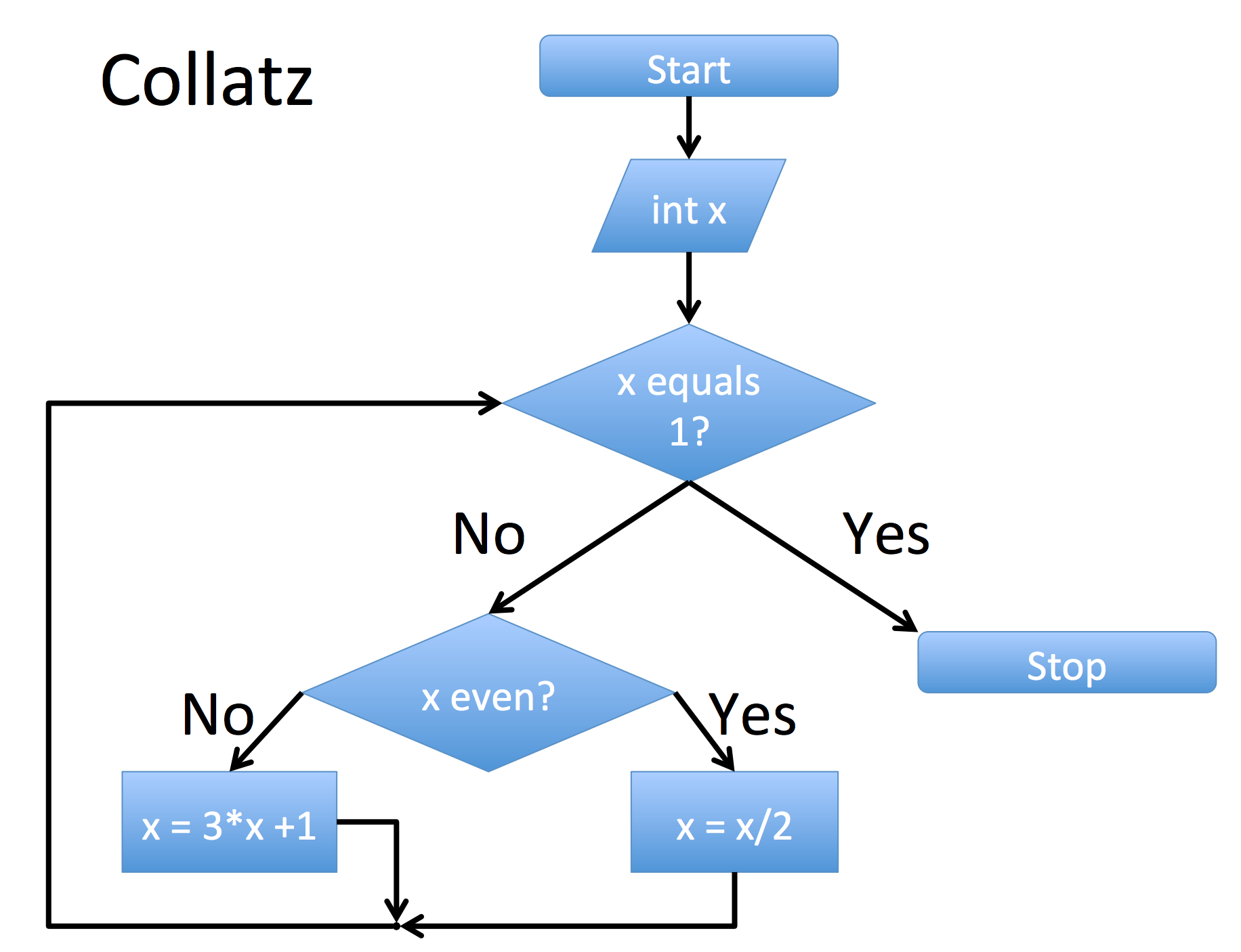
Syntax:
- After every decision you must ":" and indent (This tells python which code belongs to the yes/no part if the decision)
ex.
if x % 2 == 0:
x = x/2
else:
x = x*3+1
Check equality: "==" Assign value: "="
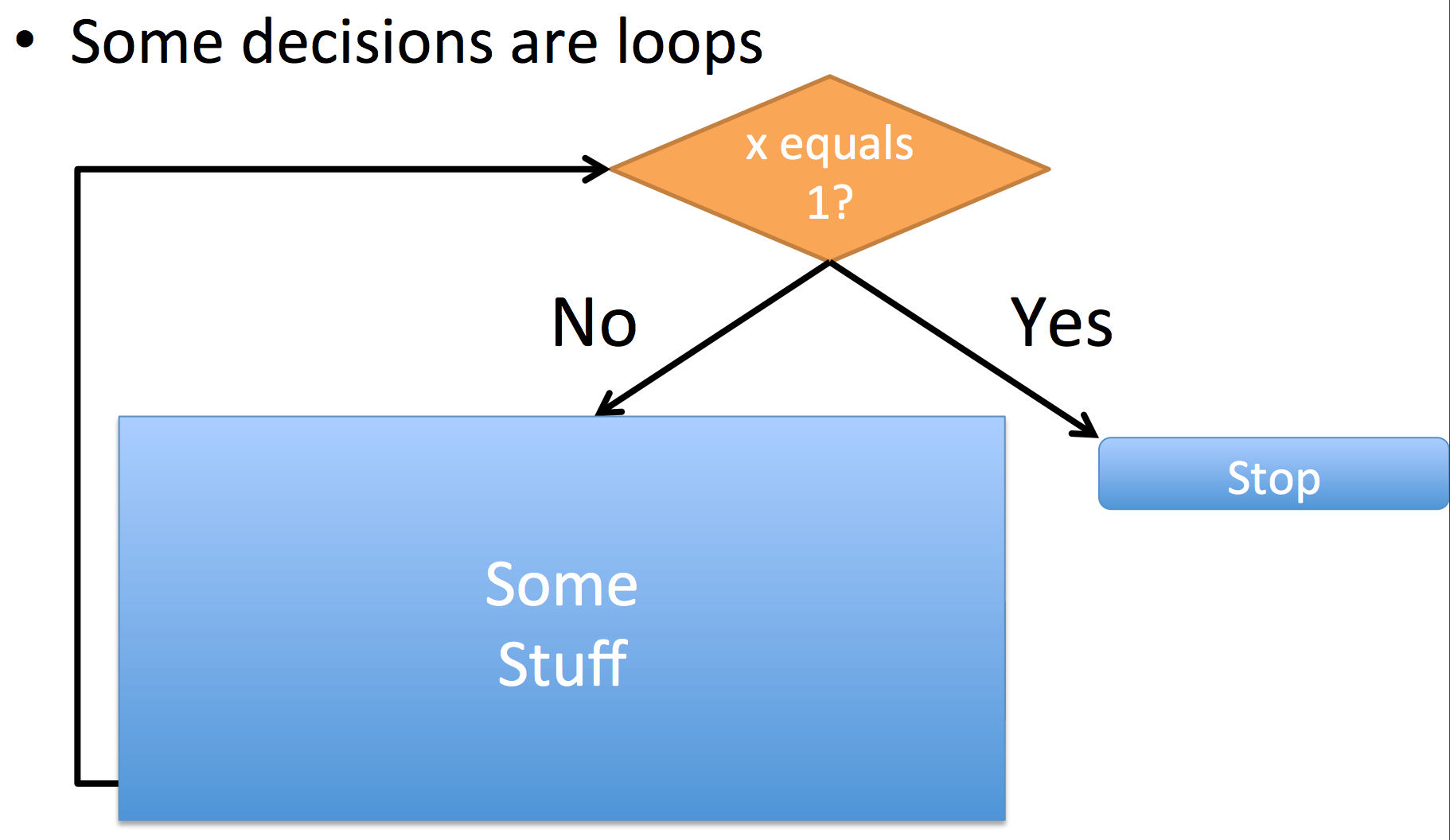
ex.
while x > 1
print("The number is %i" % x)
if x % 2 == 0:
x = x/2
else:
x = x*3+1
Nesting ^^
ex. Collatz Example
# This tells python to load a library called "time"
# Which we will use for pauses in the loop
import time
x = 5
# Keep track of the number of times through the list
loop_count = 0
# "while" is like "repeat until" in scratch, but the while loop continues until the condition is FALSE, repeat until ends once the condition is TRUE.
while x > 1:
print("The number is %i" % x)
time.sleep(1) # this waits 1 second to slow down the prints
if x % 2 == 0:
x = x/2
else:
x = x*3+1
loop_count = loop_count + 1
print("Done! It took me %i loops" % loop_count)
ex. Errors
print(test)
5 = x
print("thry this)
print("try test"
myVar = 5
print(myvar)
Google the error, and most code will return where the error is found.
ex.
def myFunction(my_number):
if my_number % 2 == 0:
print("Even!")
else:
print("Odd!")
Call the function by calling it's name
ex. myFunction(10)
ex. Functions can call other functions
def isEven(my_number):
result = False
if my_number % 2 == 0:
return = True
return result
def callFunction(my_number2):
if isEven(my_number2):
print("Even!")
else:
print("Odd!")
Recommend:
- Tutorial
- http://cscircles.cemc.uwaterloo.ca/
Lecture 18 - February 22nd, 2017
print("number is " + str(x))
str: is a function that turns a number into a string
+: concatenates the two strings
Arrays: A[j] They are list of numbers, first index of an array is 0
Selection Sort Pseudocode:
Ex. In Python
def selection_sort(A):
m = len(A)
cur_ind = m-1
while cur_ind > 0:
cur_max = -99999
#or
#cur_max = A[0]
i = 0
max_ind = 0
while i <= cur_ind:
if A[i] > cur_max:
cur_max = A[i]
max_ind = i
i = i + 1
tmp = A[cur_ind]
A[cur_ind] = A[max_ind]
A[max_ind] = tmp
cur_ind = cur_ind - 1
Demo:
A = [11,22,3,12,34,9]
print("A= "+str(A))
selection_sort(A)
print("A= "+str(A))
For Loop:
- Combine the decision and index incrementing.
- Takes care of:
- Creating a variable named i
- Incrementing it's value by one every time the loop is executed
- Compares i to N
for i in range(1,N):
Ex.
for i in range(1,5):
print(i)
1
2
3
4
---
for i in range(1, 0.5):
print(i)
Error = Expected integer, got float
Bubble Sort:
Ex. Python
def bubble_sort(A):
m = len(A)
swapped = True
while swapped == True:
swapped = False
for i in range(1,m):
if A[i-1] > A[i]
tmp = A[i]
A[i] = A[i-1]
A[i-1] = tmp
swapped = True
Demo:
A = [11,22,3,12,34,9]
print("A= "+str(A))
bubble_sort(A)
print("A= "+str(A))