Lab
Lab 1 - January 10th, 2017
Databases and SqLite
How we access data is we use these things called queries.
In the terminal type in:
sqlite3
and then
.read FILENAME.sql
and then
select * from characters;
Order matters when running select in the terminal from the database. It is not case sensitive.
Ex. You can use FROM, ChaRacters, Select, ect.
select dinstinct Applies only to what follows, and makes it so only unique data gets return.
sql
select distinct title from characters;
Notes: You can have an or in your where.
select * from characters where title = 'Horton Hears a Who' or title = 'Horton Hatches the Egg';
Ex. You can order your return.
sql
select name, year from characters order by year, title;
Aggregate function
- count
- max
- min
- avg
Lab 2 - January 17th, 2017
Flowcharts
- Rounded Rectangle -> Start and Stop
- Rectangle -> Process
- Diamond -> Decision
- Yes or No
- Italic Rectangle -> Data Input or Output
Communicate an algorithm
- Easy
- Visual
- Simple for hard problems
Criteria for lab assignment
- Flowchart:
- Draw by hand or
- Draw with https://draw.io
You should know how to:
- Convert Pseudocode to Flowchart and Flowchart to Pseudocode
Lab Exercise: Draw a flowchart for playing 1 turn of "computer pictionary"
- 2 teams (Team A and B)
- Only using names of movies
- Computer draws movie name (if it can)
- 5 guesses
N.B. Team A draws a name -> Team A inputs name into computer -> Team B guesses (Max. 5 times)
My Solution:

Group Solution:

PseudoCode Exercise: Get the name and title of books where there is a 1 and the year in lesser than 1960
Table 1: Characters
| name | title | year | human |
|---|---|---|---|
| example | example | 1983 | 1 |
| example2 | example2 | 1924 | 0 |
| example3 | example3 | 1999 | 1 |
Answer: Select name, title from characters where human=1 and year<1960
Lab 3 - January 24th, 2017
Hex to Binary To Decimal
| Dec | Hex | Binary |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0000 |
| 1 | 1 | 0001 |
| 2 | 2 | 0010 |
| 3 | 3 | 0011 |
| 4 | 4 | 0100 |
| 10 | A | 1010 |
| 11 | B | 1011 |
| 12 | C | 1100 |
| 13 | D | 1101 |
| 14 | E | 1110 |
| 15 | F | 1111 |
Binary to Hex
| 0010 | 1101 | 1111 |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | D | F |
Hex to Dec
| 2 | D | F |
|---|---|---|
| 16(2) | 16(1) | 16(0) |
= Big Number
2's compliment
Note: Number of bits need to be even
Ex: Positive number in 2's complement
+28 = 28 in binary
Lab 4 - January 31st, 2017
- OR (+)
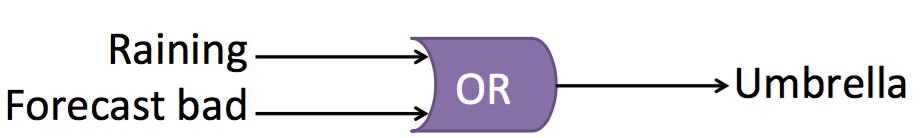
- And (*)

- XOR (circleX)
- Not (~)
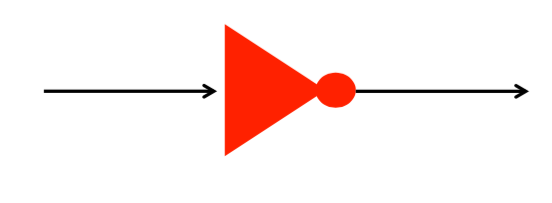
Truth Tables -> Circuit Diagram
A) Draw a diagram of an OR gate using only AND and NOT gates.
B) Draw a circuit diagram for an AND gate using only OR and NOT gates.
The "OR and ANDS" Rule
OR, AND, NOT gates
| A | B | C |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
- Look at only to inputs with 1 output.
- A is 0 -> Not gate
- B is 1 -> Nothing
- an AND those two
- A is 1 -> Nothing
- B is 1 -> Nothing
- and AND those two
- put both those paths to an OR gate
Note: Doing AND for two inputs and then AND that input with a third input is the same as AND for three inputs.
Lab 5 - February 7th, 2017
Sorting
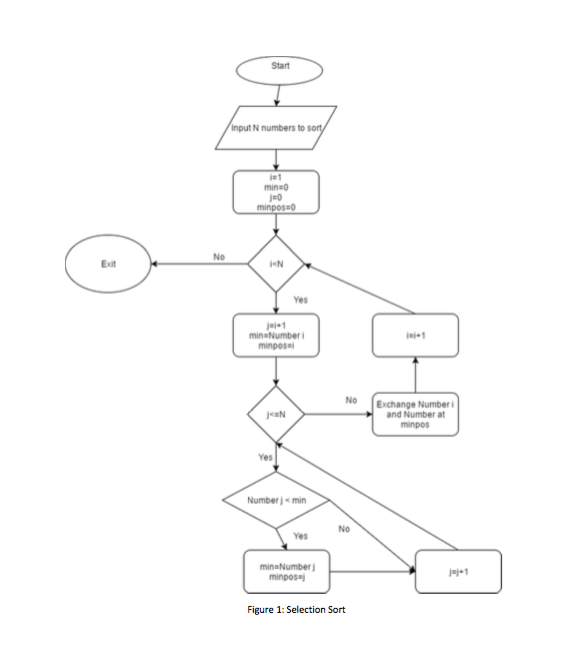
Selection Sort vs. Bubble Sort
Selection Sort
List of numbers [64, 25, 12, 22, 11]
n=5
min position = "position of min"
min = "min for index i"
i = "index for next sorted number"
j = "index to compare as next min"
1. Look at index 1
2. Find the lowest number in the list and switch it with the first position.
[11, 25, 12, 22, 64]
1. Look at index 2
2. Find the new min
3. Is the number lower than that of index 2
[11, 12, 25, 22, 64]
ect.
[11, 12, 22, 25, 64]
1. Look at the last two in the array
Bubble Sort
List of numbers [5, 1, 4, 2, 8]
n=5
i = N
j = ""
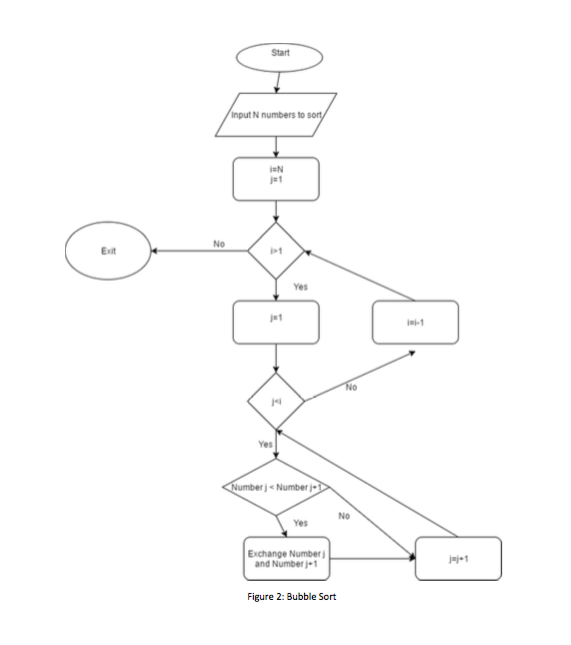
Wikipedia page on bubble sort
Lab 6 - February 21st, 2017
Human Computer Interaction
- Sign into LINUX, open chrome
- https://webdemo.balsamiq.com
- Prototype
Lab 7 - February 28th, 2017
Python Basics
In terminal:
- cd Desktop
- python python_basics.py
Basics
# commentprint "Hello World!"- Dynamically typed
def - Function
#Function
def functionName (paramaters):
code
return
- Code is linear
- For Loops
for counter in range(start num, end num, stepsize):
Lab 8 - February 7th, 2017
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/codingground.htm
fortran (https://www.tutorialspoint.com/compile_fortran_online.php)
compile -> execute Is statically typed REAL is a decimal number running the main program -> main in the terminal . is making sure there is something on either side.
! Dominique Charlebois
! Fortran Basics
! Declaring variables
REAL X, Y, SUM
! Printing
PRINT *, 'Enter X:'
! Read Command
READ *, X
PRINT *, 'Enter Y:'
READ *, Y
IF ( X .GT. Y) GO TO 100
IF ( Y .GT. X) GO TO 200
IF ( Y .EQ. X) GO TO 300
! Needed
100 PRINT *, 'X > Y'
PRINT *, 'MAX = ', X
STOP
200 PRINT *, 'Y > X'
PRINT *, 'MAX = ', Y
STOP
300 PRINT *, 'Y = X'
STOP
END
C++ https://www.tutorialspoint.com/compile_cpp_online.php compile -> execute statically typed return 0 -> this function returns an integer cout -> print something arrows to the left is send out cin -> arrows to the right is send in
// Dominique Charlebois
// C++ Basics
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "Hello World" << endl;
int X = 5;
int A = 3;
X = X + 1;
cout << "X = " << X << endl;
cout << "A = " << A << endl;
cout << "Enter a number: ";
int num1;
cin >> num1;
if (num1 > 5) {
cout << num1 << " is greater than 5" << endl;
} else {
cout << num1 << " is less than 5" << endl;
}
for (int i = num1; i >= 0; i--) {
cout << i << endl;
}
cout << " Blast Off!" << endl;
return 0;
}
go created by google python and java statically typed (Kindof) execute
// Domininque Charlebois
// Google Go Basics
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Printf("hello, world\n")
var hello string = "Hello World!"
var a int = 3
// More of dynamically typed
x := 5
fmt.Println(hello, a, x)
var num int
fmt.Print("Enter a number: ")
// REading input from the command line, storing integer as num variable
fmt.Scanf("%d", &num)
if num > x {
fmt.Println(num, " is larger than 5")
} else if num < x {
fmt.Println(num, " is lesser than 5")
} else {
// Enter this code block only when num entered is = 5
fmt.Println(num, " is equal to 5")
}
for i := 5; i > 0; i-- {
// Execute Code
fmt.Println(i)
}
fmt.Println("Blast Off!")
}